Frogs are incredibly diverse amphibians found in forests, deserts, mountains, wetlands, and even human neighborhoods. With a wide range of colors, sizes, and behaviors, each species plays an important role in its ecosystem. Below is a collection of 42 unique frog species from around the world, showcasing their remarkable adaptations, appearances, and habitats.
1. American Bullfrog

The American Bullfrog is one of the largest and most recognizable frogs in North America. Known for its deep booming call and impressive size, it thrives in ponds, lakes, and slow-moving waters. This species is adaptable, widespread, and plays an important role in wetland ecosystems.
Identification
- Large, robust body with smooth green to olive skin
- Distinct tympanum (eardrum) larger than the eye in males
- Powerful hind legs built for strong leaps
- Yellow throat in adult males during breeding season
Size
Adult American Bullfrogs typically measure 3.5 to 8 inches in body length, making them one of the biggest frog species in the region. Their strong legs and muscular bodies contribute to their hefty and noticeable appearance.
Habitat
They prefer warm, permanent bodies of freshwater such as lakes, ponds, marshes, slow streams, and reservoirs. Abundant vegetation around the shoreline provides cover and hunting opportunities.
Behavior
American Bullfrogs are opportunistic predators, feeding on insects, small fish, snakes, other frogs, and even small mammals. They are known for their loud mating calls, especially during warm evenings in summer, and are active primarily from late spring through early fall.
2. Green Tree Frog

The Green Tree Frog is a small, bright, and agile species commonly found in the southeastern United States. Its vibrant coloration and distinctive calls make it a familiar sight in wetlands, backyards, and humid forested areas.
Identification
- Smooth bright green skin with occasional yellow spots
- Long slender limbs with adhesive toe pads
- White or cream stripe running from jaw to groin
- Small, slim body ideal for climbing vegetation
Size
Green Tree Frogs typically measure 1.5 to 2.5 inches in length. Their lightweight body and elongated limbs allow them to cling easily to leaves, stems, and windows.
Habitat
They inhabit swamps, marshes, wet forests, and gardens, especially areas with abundant vegetation near water. They are often found perched on reeds, shrubs, and even outdoor lights.
Behavior
Green Tree Frogs are mostly nocturnal, feeding on insects attracted to light. Males produce a loud, repetitive call during the breeding season. They are agile climbers and rely on camouflage to avoid predators.
3. Red-Eyed Tree Frog

The Red-Eyed Tree Frog is an iconic tropical species known for its vivid colors and striking appearance. Native to Central America, it thrives in humid rainforests and is a symbol of biodiversity in the region.
Identification
- Bright green body with blue and yellow flank markings
- Large, vivid red eyes with vertical pupils
- Orange or red feet with strong adhesive toe pads
- Smooth skin and slender limbs suited for climbing
Size
Red-Eyed Tree Frogs typically measure 2 to 3 inches in length. Their lightweight frame allows effortless movement through leaves and branches.
Habitat
They live in lowland tropical rainforests, staying close to water sources such as ponds and slow streams where they breed. They prefer dense vegetation with high humidity.
Behavior
This species is nocturnal and relies heavily on camouflage during the day. When threatened, they use a “startle display” by flashing their red eyes and bright flanks to confuse predators. They primarily feed on insects and small invertebrates.
4. Poison Dart Frog
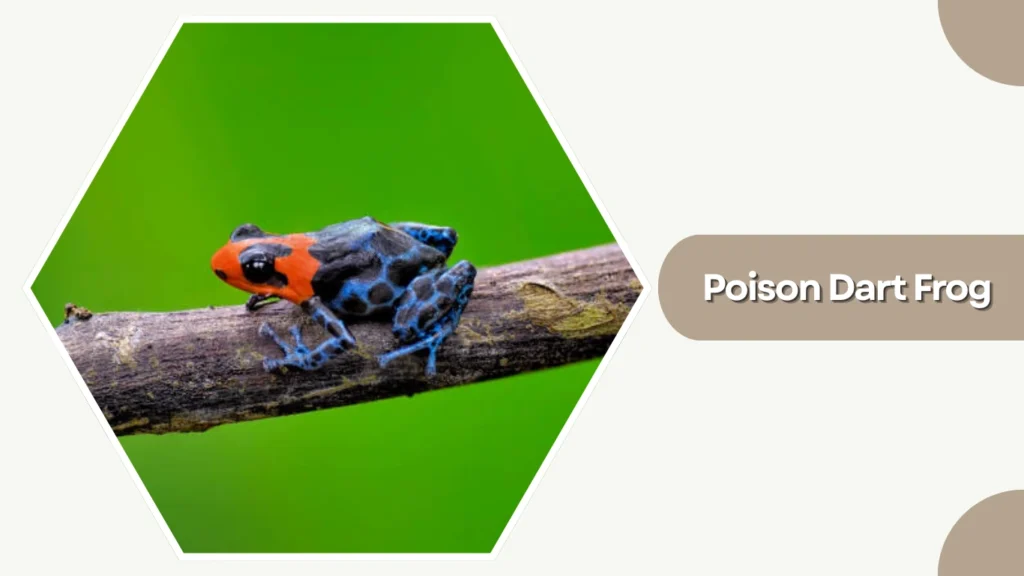

Poison Dart Frogs are small, brilliantly colored amphibians native to Central and South American rainforests. Their vivid patterns serve as a warning to predators about their potent skin toxins.
Identification
- Bright colors such as blue, yellow, red, or orange
- Smooth skin with bold patterns or spots
- Small, compact body structure
- Visible warning coloration signaling toxicity
Size
Most Poison Dart Frogs measure 1 to 2 inches in length, though some species may be slightly smaller or larger. Their tiny bodies are lightweight and agile, ideal for navigating dense forest floors and vegetation.
Habitat
They inhabit humid tropical rainforests, often near streams, leaf litter, and mossy ground. Moist environments are essential for maintaining their skin hydration and reproductive behaviors.
Behavior
Poison Dart Frogs are diurnal, active during daylight hours. They are territorial and vocal, especially during breeding. Their toxicity comes from alkaloid chemicals derived from their natural diet of ants, mites, and small insects.
5. African Clawed Frog
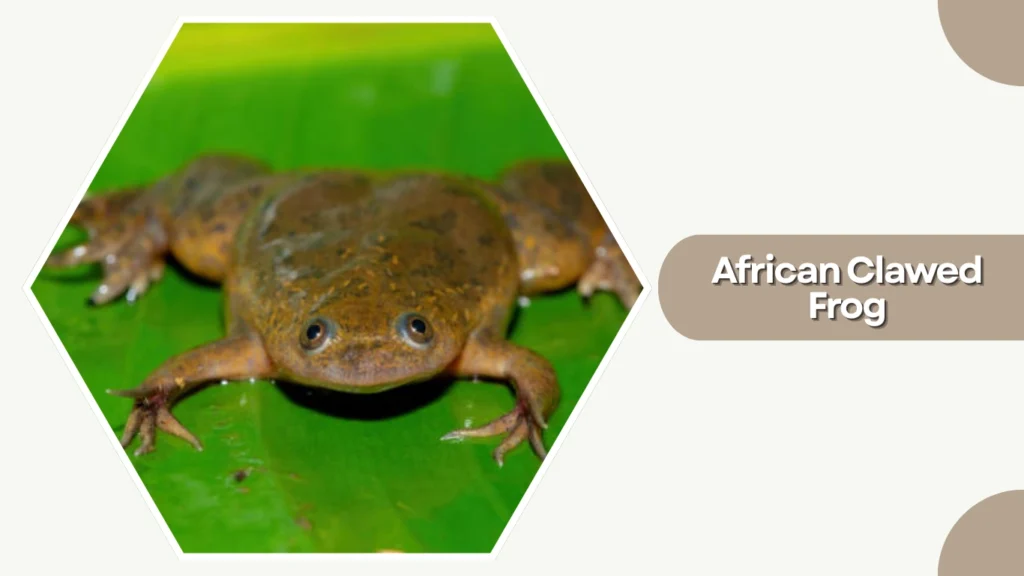

The African Clawed Frog is an aquatic species native to sub-Saharan Africa, known for its fully webbed feet and claw-tipped toes. It thrives in still or slow-moving freshwater environments and is widely used in scientific research.
Identification
- Smooth, mottled brown or olive skin
- Flattened body with fully webbed hind feet
- Three short black claws on each hind foot
- Eyes positioned on top of the head for surface vision
Size
African Clawed Frogs typically measure 2 to 5 inches in length. Their wide, flat bodies and powerful legs make them excellent swimmers adapted for fully aquatic life.
Habitat
They live in ponds, marshes, stagnant water, and slow streams, often hiding in mud or vegetation. They can tolerate poor water quality and survive drought by burrowing.
Behavior
This species is fully aquatic, feeding on insects, small fish, and organic matter. They use a unique method of sensing vibrations to locate prey. They are active, hardy, and capable of producing clicking calls underwater.
6. Pacman Frog

The Pacman Frog is a stout, round-bodied amphibian known for its large mouth and voracious appetite. Native to South America, it is a popular pet due to its unique appearance and minimal activity.
Identification
- Large, rounded body with a wide mouth
- Bright patterns in green, brown, yellow, or orange
- Short limbs compared to body size
- Distinct horn-like projections above the eyes in some species
Size
Pacman Frogs typically measure 4 to 7 inches in length. Their bulky form and enormous mouths allow them to consume prey nearly as large as themselves.
Habitat
They inhabit humid forest floors, leaf litter, and marshy areas in tropical South America. Moist environments with plenty of hiding spots suit them best.
Behavior
Pacman Frogs are ambush predators, remaining still and striking quickly at passing prey. They are solitary, territorial, and spend most of their time buried with only their eyes exposed, waiting to feed.
7. Tomato Frog
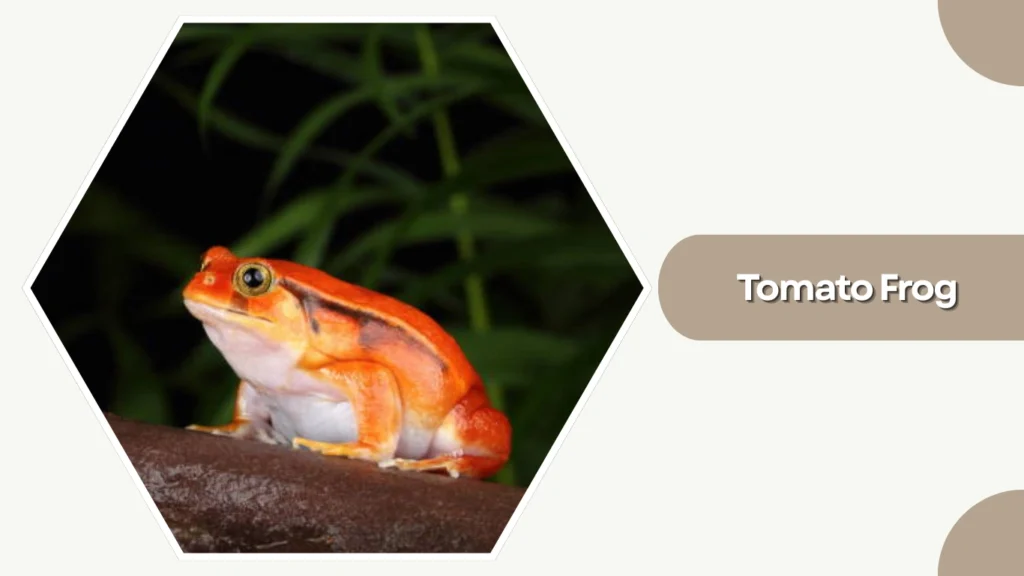

The Tomato Frog is a vividly colored species from Madagascar, known for its bright red or orange appearance. Its bold coloration serves as a warning to predators, and it thrives in humid, lowland environments.
Identification
- Bright red, orange, or tomato-like coloration
- Rounded, plump body shape
- Smooth skin with minimal patterning
- Short limbs and a broad head
Size
Tomato Frogs typically measure 2.5 to 4 inches in length. Their rounded bodies contribute to their distinctive, inflated appearance.
Habitat
They inhabit rainforests, marshy areas, and moist ground in Madagascar. They prefer environments with abundant leaf litter and soft soil for burrowing.
Behavior
Tomato Frogs are nocturnal ambush predators, feeding on insects and small invertebrates. When threatened, they can secrete a sticky, milky toxin to deter predators. They often inflate their bodies to appear larger.
8. Glass Frog

Glass Frogs are delicate, small amphibians native to Central and South America, famous for their translucent undersides that reveal internal organs. They inhabit lush, humid forest environments near streams.
Identification
- Lime-green upper body with smooth skin
- Translucent belly showing organs
- Slender limbs with adhesive toe pads
- Large eyes facing forward
Size
Glass Frogs typically measure 1.2 to 3 inches in length. Their lightweight, delicate build allows easy movement across leaves and branches.
Habitat
They are found in tropical rainforests near clear, fast-moving streams, where they lay eggs on leaves overhanging water. High humidity and dense vegetation are essential.
Behavior
Glass Frogs are mostly nocturnal, remaining hidden during the day. Males guard egg clutches and call from leaves above streams. They feed on small insects and larvae while staying close to flowing water.
9. Spring Peeper
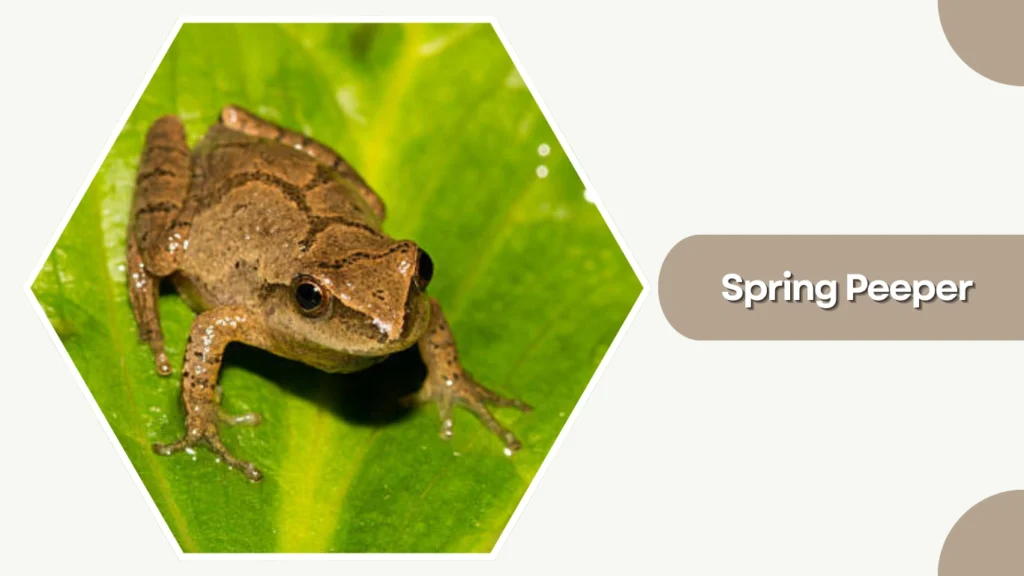

The Spring Peeper is a tiny chorus frog native to eastern North America, celebrated for its distinctive high-pitched call that signals the arrival of spring. Despite its small size, it plays a large role in wetland ecosystems.
Identification
- Tan, brown, or gray coloration with a dark “X” on the back
- Small, slender body with smooth skin
- Slightly enlarged toe pads for climbing
- Dark line through the eye
Size
Spring Peepers typically measure 0.75 to 1.5 inches in length. Their tiny bodies allow them to hide easily among vegetation and leaf litter.
Habitat
They inhabit woodlands, marshes, ponds, and damp forest floors, especially areas with temporary or shallow water for breeding. They stay hidden in vegetation to avoid predators.
Behavior
Spring Peepers are most active at dusk and night, forming loud breeding choruses in early spring. Their “peep” calls can be heard from long distances. They feed on small insects and are highly sensitive to moisture levels.
10. Gray Tree Frog
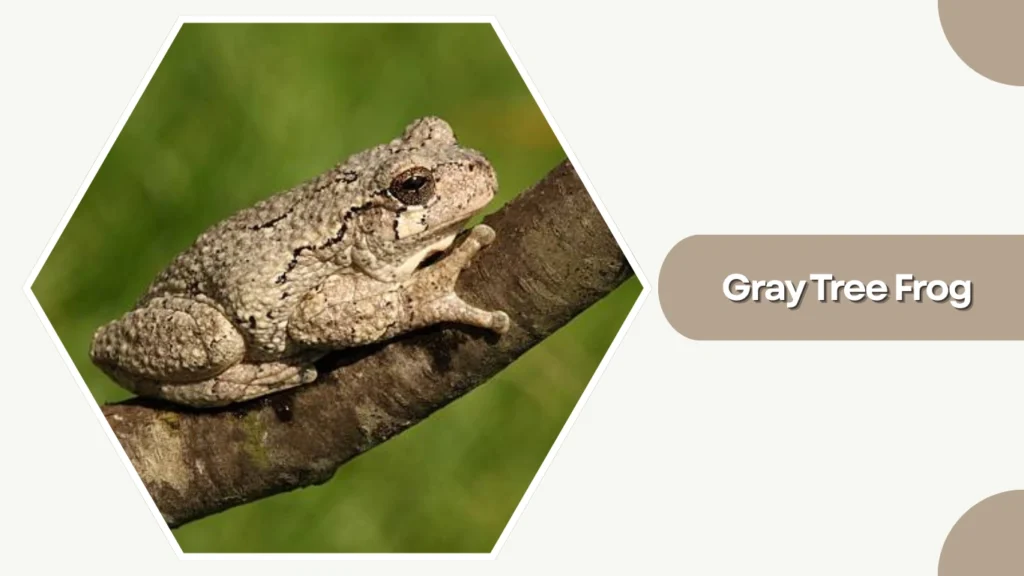

The Gray Tree Frog is a highly adaptable amphibian found across much of the eastern United States. Known for its remarkable ability to change color, it blends easily with tree bark and foliage.
Identification
- Gray, green, or brown skin that changes with environment
- Rough, warty texture
- Large toe pads for strong climbing grip
- Bright orange or yellow patch on inner thighs
Size
Gray Tree Frogs typically measure 1.25 to 2 inches in length. Their compact size and strong limbs make them excellent climbers.
Habitat
They inhabit woodlands, swamps, backyards, and forest edges, usually near temporary or permanent water sources. They spend much of their time high in trees.
Behavior
Gray Tree Frogs are nocturnal, calling loudly during warm, humid nights. They are solitary and rely on camouflage to avoid predators. Their diet consists mainly of insects and small invertebrates.
11. Cuban Tree Frog

The Cuban Tree Frog is a large, invasive tree frog species originally from the Caribbean but now widespread in parts of Florida. Its adaptability and rapid reproduction allow it to thrive in many environments.
Identification
- Warty skin in shades of gray, brown, or green
- Large toe pads for strong climbing ability
- Often has a mottled or blotchy pattern
- Notably large size compared to other tree frogs
Size
Cuban Tree Frogs typically measure 2 to 5 inches in length. Their sizable bodies and strong climbing limbs contribute to their dominance in introduced areas.
Habitat
They inhabit urban areas, forests, wetlands, and residential zones, often hiding in vegetation, pipes, crevices, and outdoor structures. They tolerate a wide range of moisture and temperature conditions.
Behavior
Cuban Tree Frogs are nocturnal predators, feeding on insects, smaller frogs, and even small reptiles. They are known for their loud, raspy calls and their tendency to outcompete native species.
12. White’s Tree Frog
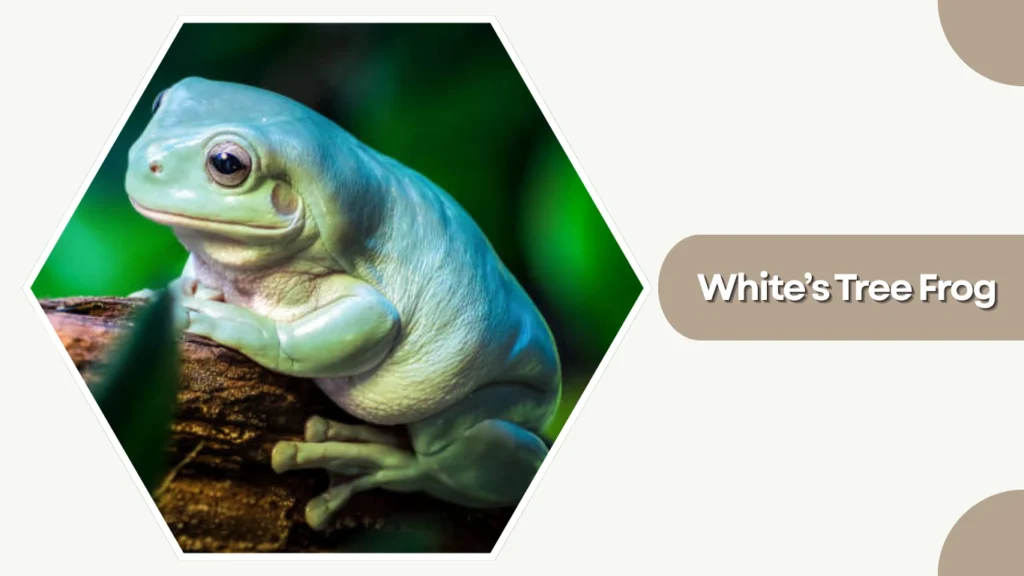

White’s Tree Frog, also known as the Dumpy Tree Frog, is a calm and sturdy species native to Australia and New Guinea. Its gentle temperament makes it a popular choice for amphibian enthusiasts.
Identification
- Smooth, green or blue-green skin with a waxy appearance
- Chubby body with a rounded face
- Large toe pads for climbing
- Occasional white spots or patches along the back
Size
White’s Tree Frogs typically measure 3 to 4.5 inches in length. Their plump bodies and relaxed posture give them a distinctive, “dumpy” look.
Habitat
They inhabit rainforests, wet woodlands, and even human dwellings, often found in trees, shrubs, and sheltered structures. They prefer warm, humid environments but tolerate drier conditions well.
Behavior
White’s Tree Frogs are docile and nocturnal, feeding on insects and small invertebrates. They often perch in exposed areas and are known for their calm, almost sluggish demeanor. They also produce soft, croaking calls, especially during breeding season.
13. Goliath Frog
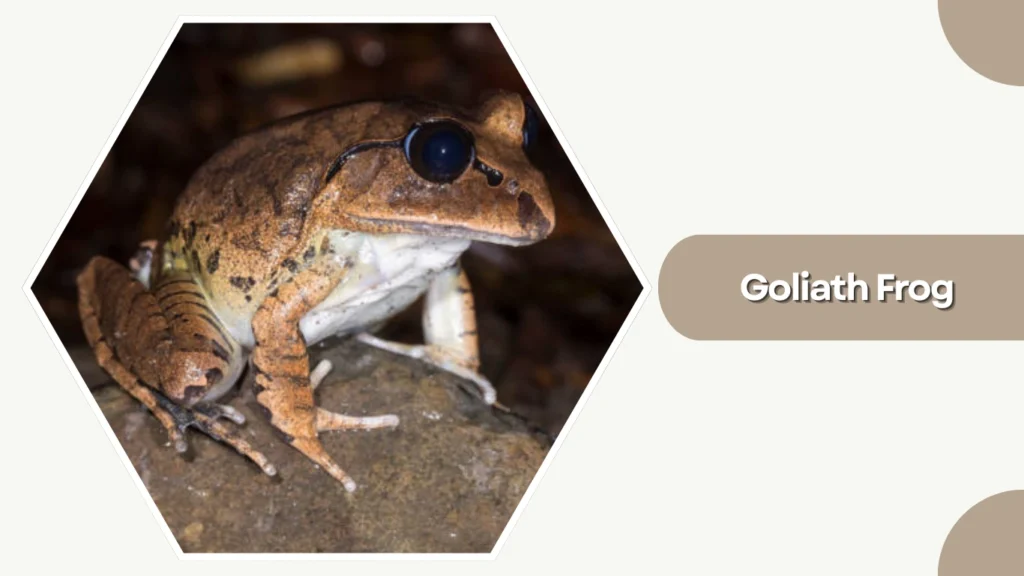

The Goliath Frog is the largest frog species in the world, native to West Africa. Known for its massive size and powerful build, it inhabits fast-flowing rivers and rocky streams.
Identification
- Olive-green to brown coloration with rough skin
- Extremely large, muscular body
- Strong, long hind legs
- Broad head with prominent eyes
Size
Goliath Frogs typically measure 12.5 inches in length and can weigh over 7 pounds. Their immense size sets them apart from all other frog species.
Habitat
They live in swift rivers, waterfalls, and rocky forest streams in Cameroon and Equatorial Guinea. Clean, oxygen-rich water is essential for their survival.
Behavior
Goliath Frogs are powerful jumpers and strong swimmers, feeding on insects, crustaceans, and small vertebrates. They are shy, primarily nocturnal, and known to build nests by moving stones to create suitable breeding sites.
14. Wood Frog

The Wood Frog is a hardy amphibian native to North America, famous for its ability to survive freezing temperatures. It inhabits forested regions and is well-adapted to seasonal climates.
Identification
- Brown, tan, or rust-colored body
- Distinct dark “mask” across the eyes
- Smooth skin with subtle mottling
- Slender limbs and a pointed snout
Size
Wood Frogs typically measure 1.5 to 3 inches in length. Their lightweight build helps them move efficiently through forest floors and leaf litter.
Habitat
They inhabit forests, wetlands, bogs, and moist woodland edges, often far from permanent bodies of water. They use temporary pools for breeding in early spring.
Behavior
Wood Frogs are seasonally active, known for their freeze tolerance during winter. They feed on insects and small invertebrates and produce a duck-like call during mating season.
15. Northern Leopard Frog
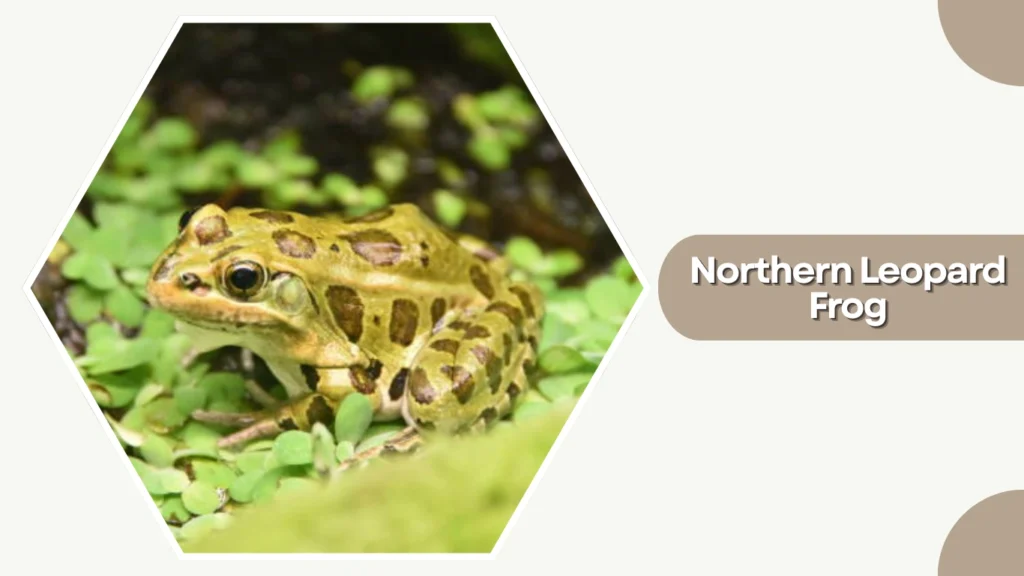

The Northern Leopard Frog is a widespread North American species recognized for its distinctive spots and agile movements. It thrives in a variety of wetland habitats and is often seen near grassy fields and ponds.
Identification
- Green or brown body with dark, rounded leopard-like spots
- Light dorsal ridge running down each side of the back
- Smooth skin with sleek, slender build
- Long powerful hind legs for jumping
Size
Northern Leopard Frogs typically measure 2 to 4.5 inches in length. Their athletic build allows them to leap long distances and move quickly through vegetation.
Habitat
They inhabit marshes, ponds, meadows, slow streams, and grassy wetlands. They prefer areas with abundant vegetation and access to both land and water.
Diet
Northern Leopard Frogs feed on insects, spiders, worms, small crustaceans, and occasionally smaller frogs. They actively hunt along water edges and in grassy areas, using quick jumps and a sticky tongue to capture prey.
16. Southern Leopard Frog

The Southern Leopard Frog is a common amphibian across the southeastern United States. Known for its spotted pattern and strong jumping ability, it thrives in warm, moist environments.
Identification
- Light green to brown body with dark oval spots
- Distinct light stripe along the upper jaw
- Smooth skin with slim build
- Prominent dorsal ridges running down the back
Size
Southern Leopard Frogs typically measure 2 to 3.5 inches in length. Their lean, muscular legs enable quick movement on land and in shallow water.
Habitat
They inhabit ditches, ponds, marshes, swamps, and wet meadows, often remaining close to shallow freshwater. They adapt well to both natural and disturbed habitats.
Diet
Southern Leopard Frogs feed on insects, small crustaceans, snails, worms, and small invertebrates, actively foraging along water margins and grassy areas.
17. Pickerel Frog
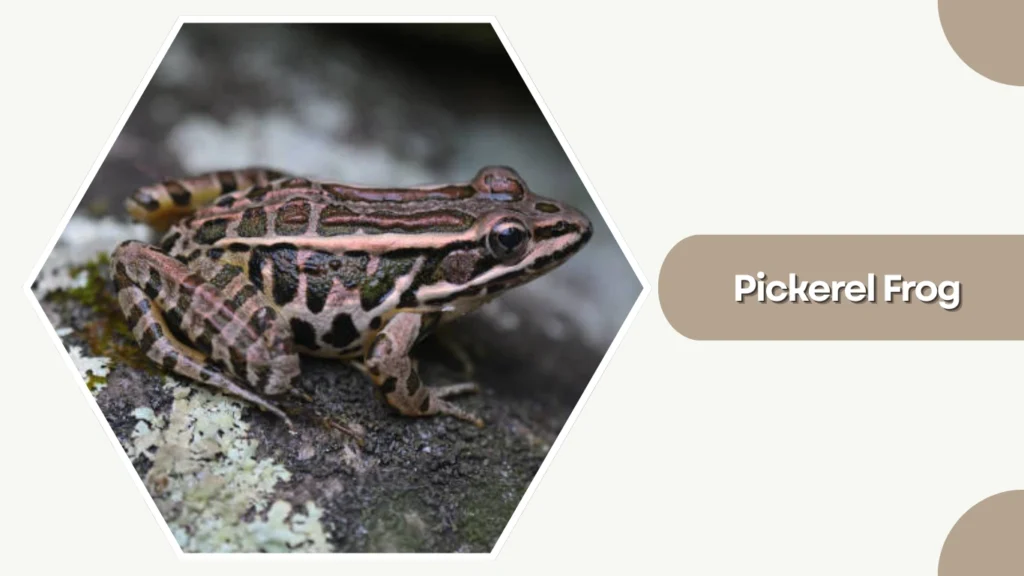

The Pickerel Frog is a medium-sized frog native to North America, recognized for its distinctive rectangular spots and mild toxic secretions that deter predators. It prefers cool, clean water environments.
Identification
- Tan or brown body with paired rectangular dark spots
- Bright yellow or orange inner thighs
- Smooth skin with slender form
- Prominent dorsolateral folds along the back
Size
Pickerel Frogs typically measure 1.75 to 3 inches in length. Their streamlined bodies help them move quickly through cool streams and grassy areas.
Habitat
They inhabit clear streams, springs, meadows, wetlands, and forested ponds, often preferring cooler climates and unpolluted water sources.
Diet
Pickerel Frogs feed on insects, spiders, small crustaceans, worms, and other invertebrates, actively hunting along water edges and moist grasslands.
18. Mink Frog
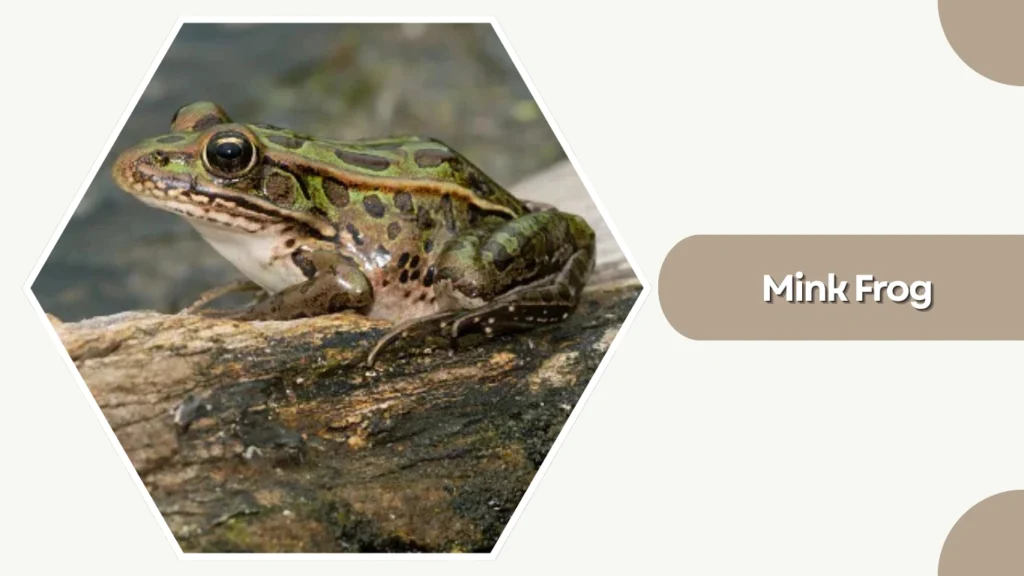

The Mink Frog is a semi-aquatic species native to the northern United States and Canada. Known for its musky, mink-like odor, it thrives in cool, heavily vegetated aquatic habitats.
Identification
- Greenish to brown body with mottled or blotchy patterns
- Smooth skin with subtle dark patches
- Webbed hind feet suited for strong swimming
- Blunt snout and relatively small size
Size
Mink Frogs typically measure 1.75 to 2.75 inches in length. Their compact build allows them to move easily among dense aquatic plants.
Habitat
They inhabit lakes, ponds, bogs, and slow-moving streams with abundant vegetation, especially in cooler northern regions.
Diet
Mink Frogs feed on insects, aquatic invertebrates, small crustaceans, and larvae, hunting both at the water’s surface and among underwater vegetation.
19. Barking Tree Frog
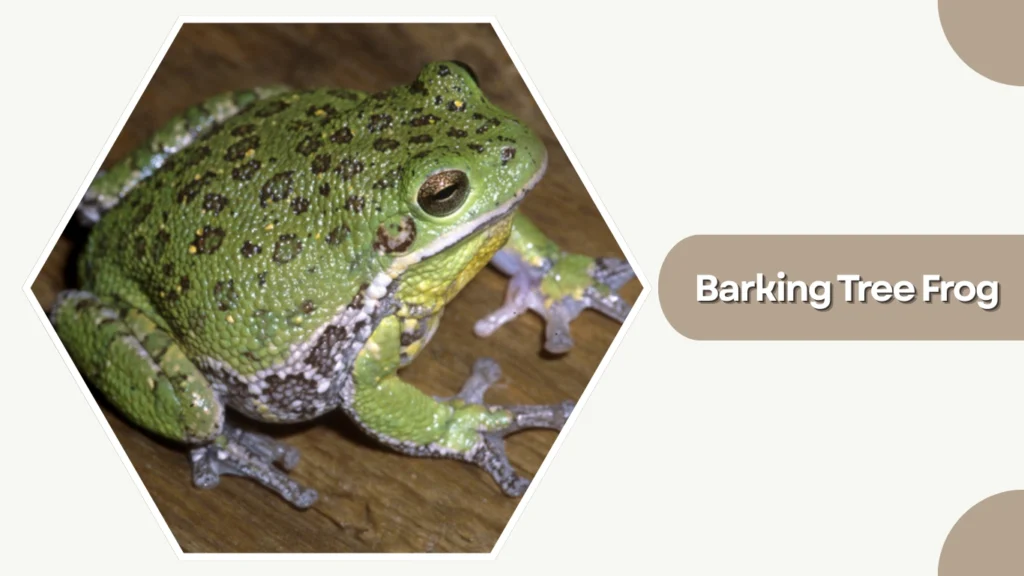

The Barking Tree Frog is the largest native tree frog in the southeastern United States. Its name comes from its loud, dog-like call that can carry across long distances, especially during warm, humid nights.
Identification
- Bright green to brown body, often with round darker spots
- Smooth or slightly granular skin texture
- Large, rounded toe pads for excellent climbing
- Plump, robust body with noticeable skin folds on the sides
Size
Barking Tree Frogs typically measure 2 to 2.75 inches in length. Their stout build and strong limbs make them highly adaptable to both arboreal and terrestrial life.
Habitat
They inhabit pine forests, swamps, wetlands, riverbanks, and coastal plains, often staying high in trees during the day. They also use sandy burrows and leaf litter for shelter during dry periods. Breeding takes place in temporary ponds and shallow wetlands.
Diet
Barking Tree Frogs feed on insects, spiders, moths, beetles, crickets, caterpillars, and small invertebrates. They are active nighttime hunters, waiting on vegetation or tree branches to ambush prey attracted to movement or light.
20. Canyon Tree Frog
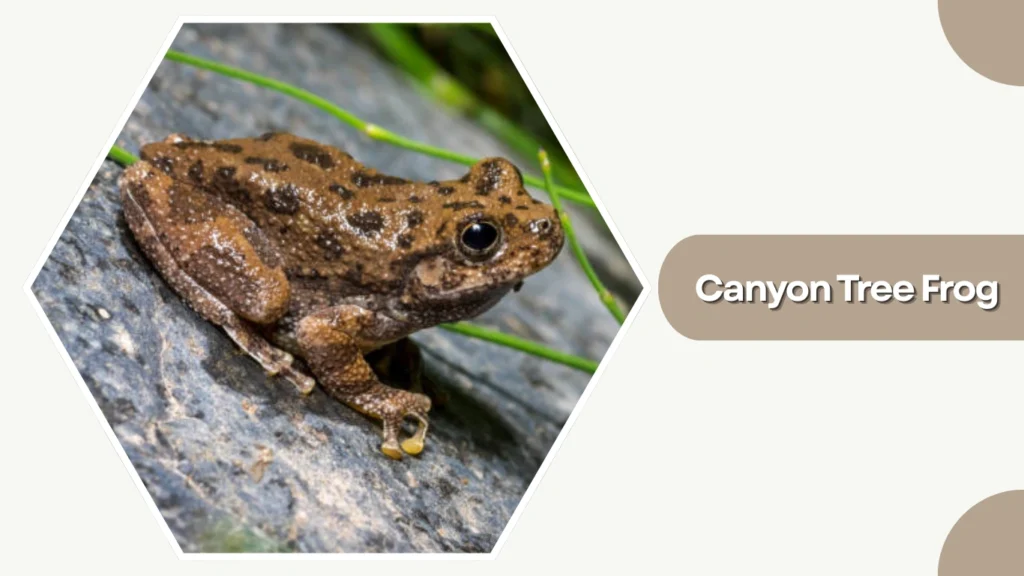

The Canyon Tree Frog is a camouflaged, rock-dwelling species native to the southwestern United States and northern Mexico. Its coloration helps it blend seamlessly with rocky surroundings, making it difficult to spot.
Identification
- Gray, brown, or tan skin matching surrounding rock colors
- Rough, granular texture for better camouflage
- Round toe pads for climbing rock surfaces
- Compact body with subtle pattern variations
Size
Canyon Tree Frogs typically measure 1.25 to 2.25 inches in length. Their small, sturdy build allows them to maneuver easily across rocky terrain.
Habitat
They inhabit rocky canyons, cliffs, desert streams, waterfalls, and boulder-filled riverbeds. They prefer moist cracks, crevices, and shaded rock surfaces near water, retreating into tight spaces during heat or drought.
Diet
Canyon Tree Frogs feed on insects, flies, ants, beetles, spiders, and small invertebrates, often hunting at night along rock surfaces or near water sources.
21. Golden Mantella

The Golden Mantella is a small, brilliantly colored frog native to Madagascar. Known for its bright orange or yellow hue, it is one of the most striking and endangered amphibians in the world.
Identification
- Vibrant orange, yellow, or reddish coloration
- Smooth skin with no markings or patterns
- Small, slender body with delicate limbs
- Black, beady eyes providing sharp contrast
Size
Golden Mantellas typically measure 0.75 to 1 inch in length. Their tiny size and vivid coloration make them both eye-catching and easily recognizable.
Habitat
They inhabit rainforests, swampy forest floors, and mossy, humid areas with abundant leaf litter. They rely on moist microhabitats and are often found near temporary pools or marshy clearings.
Diet
Golden Mantellas feed on ants, mites, springtails, termites, and tiny invertebrates. Their diet is believed to contribute to the alkaloid toxins present in their skin.
22. Oriental Fire-Bellied Toad

The Oriental Fire-Bellied Toad is a brightly colored amphibian native to northeastern Asia. Its striking red or orange belly serves as a warning to predators about its mild skin toxins.
Identification
- Bright green back with black mottled spots
- Vivid red or orange belly with irregular dark markings
- Warty, bumpy skin texture
- Triangular-shaped pupils and webbed hind feet
Size
Oriental Fire-Bellied Toads typically measure 1.5 to 2.5 inches in length. Their compact, rounded bodies make them easy swimmers and agile movers.
Habitat
They inhabit ponds, marshes, slow streams, rice paddies, and forest edges, preferring shallow waters with plenty of vegetation. They often bask on floating plants and logs.
Diet
Oriental Fire-Bellied Toads feed on insects, worms, snails, small crustaceans, and other small invertebrates, actively hunting in both water and on land.
23. Surinam Toad
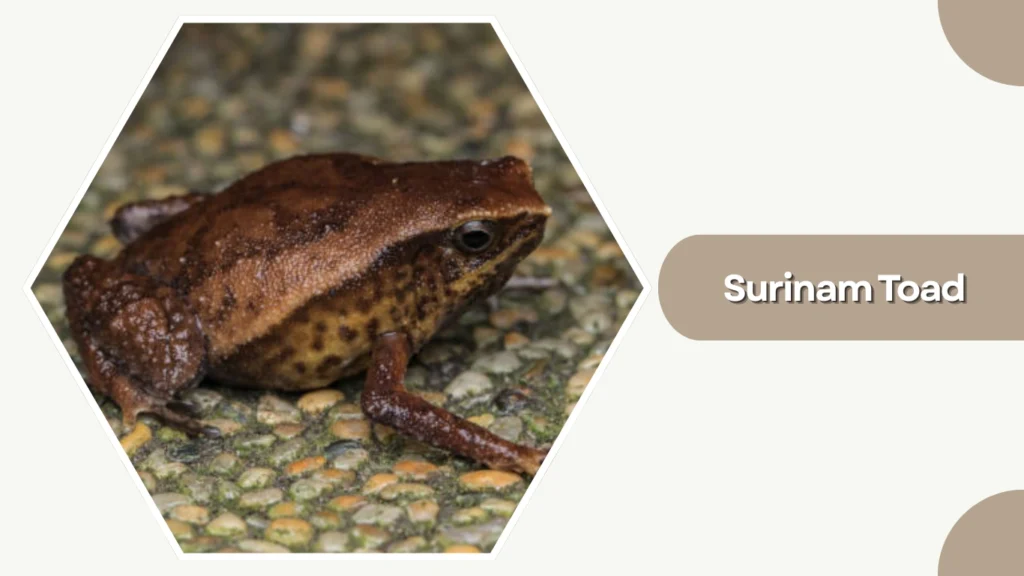

The Surinam Toad is an unusual, fully aquatic amphibian from South America, famous for its flat, leaf-like body and unique reproductive method, where eggs develop in pockets on the female’s back.
Identification
- Flat, triangular-shaped body resembling a dead leaf
- Brown or gray mottled skin for camouflage
- Limbs with star-shaped fingertips
- Small eyes positioned on top of the head
Size
Surinam Toads typically measure 4 to 8 inches in length. Their flattened bodies help them blend into muddy or leaf-covered pond bottoms.
Habitat
They inhabit slow-moving rivers, ponds, marshes, and muddy freshwater environments across northern South America. They remain underwater almost their entire lives.
Diet
Surinam Toads feed on small fish, worms, aquatic insects, crustaceans, and larvae, using a rapid suction-feeding method rather than a tongue.
24. Amazon Milk Frog
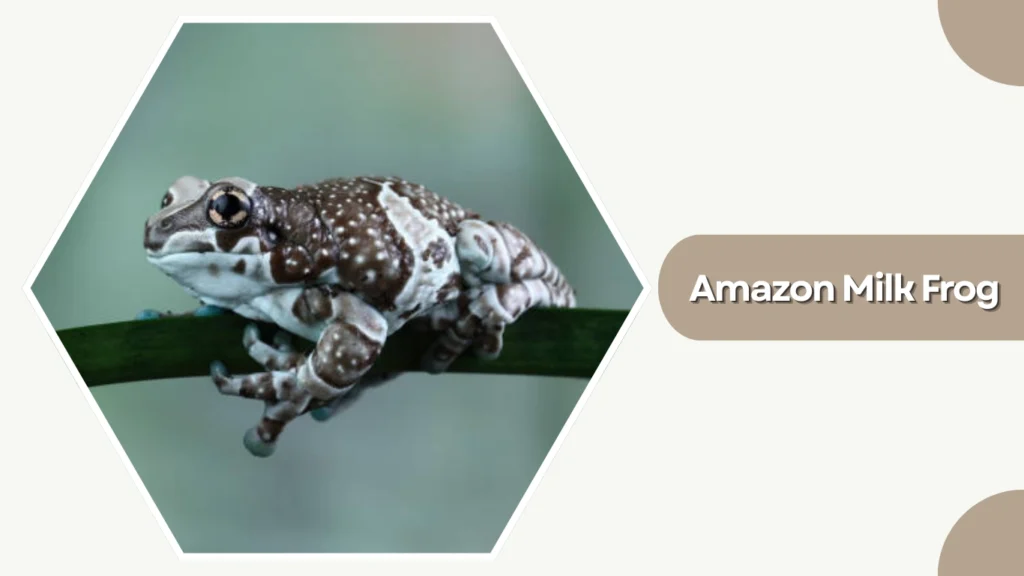

The Amazon Milk Frog, also known as the Mission Golden-Eyed Tree Frog, is a large arboreal species native to the Amazon Basin. It gets its name from the milky secretion it produces when stressed, which helps deter predators. This frog is admired for its striking patterns and calm temperament.
Identification
- Light gray body with dark brown or black banded markings
- Slightly bumpy skin texture
- Large golden eyes with vertical pupils
- Strong toe pads for climbing high in trees
Size
Amazon Milk Frogs typically measure 2.5 to 4 inches in length, with females generally larger than males. Their sturdy build supports an active arboreal lifestyle.
Habitat
They inhabit humid tropical rainforests near rivers, flooded forests, and canopy vegetation. They prefer consistently warm, wet environments and often shelter in tree holes.
Diet
Amazon Milk Frogs feed on insects, spiders, larvae, small invertebrates, and occasional small vertebrates, using their sticky tongues to catch prey at night.
25. Strawberry Poison Dart Frog
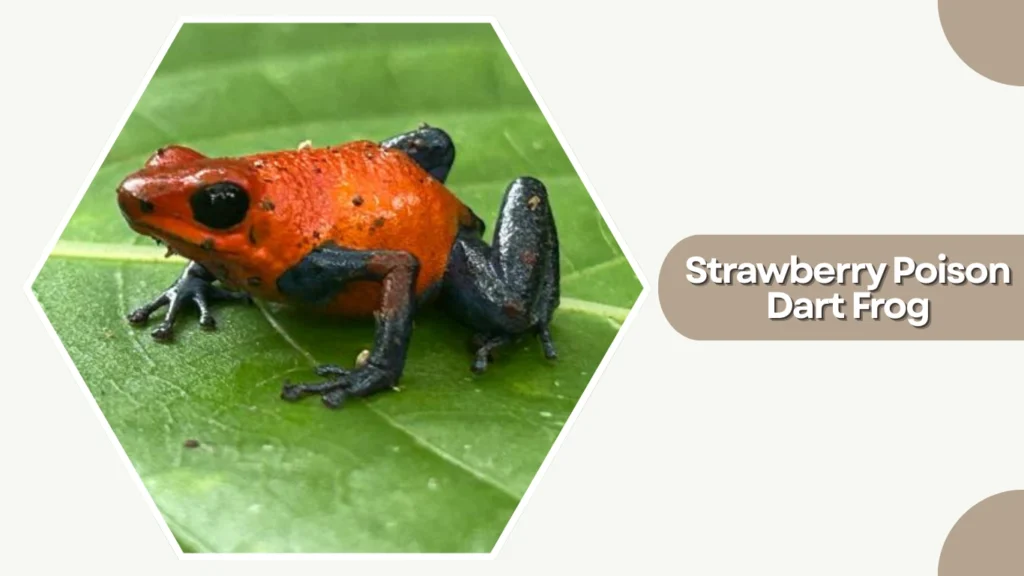

The Strawberry Poison Dart Frog is a vibrant and highly variable species native to Central America, especially Costa Rica and Panama. Its bright coloration serves as a warning of its toxicity, and it is well-known for its diverse morphs, displaying different colors across regions.
Identification
- Bright red or orange body resembling a strawberry
- Blue or black limbs depending on the morph
- Smooth skin with a compact, rounded body
- Small size with agile, quick movements
Size
Strawberry Poison Dart Frogs typically measure 0.75 to 1 inch in length. Despite their tiny size, they are bold and highly active.
Habitat
They inhabit tropical rainforests, humid lowlands, mossy forest floors, and areas near small streams, often hiding under leaves, logs, and bromeliads. They prefer wet microhabitats with stable humidity.
Diet
Strawberry Poison Dart Frogs feed on ants, mites, tiny beetles, springtails, and other minute invertebrates. Their specialized diet contributes to the alkaloid toxins found in their skin.
26. Blue Poison Dart Frog
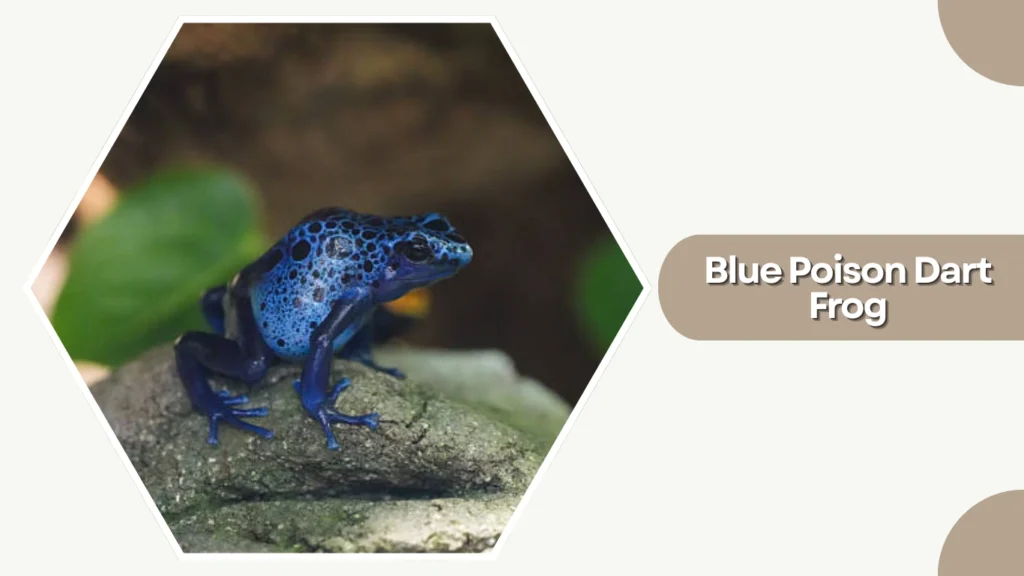

The Blue Poison Dart Frog is one of the most visually striking amphibians, native to a small region in Suriname. Its vivid blue coloration with black spots makes it both beautiful and highly recognizable. This species is toxic in the wild, using its bright colors to warn predators.
Identification
- Vibrant blue body with irregular black spots
- Smooth, glossy skin
- Compact body with delicate limbs
- Rounded toes without extensive webbing
Size
Blue Poison Dart Frogs typically measure 1 to 1.8 inches in length. Their small, lightweight bodies allow them to move swiftly through forest floors and leaf litter.
Habitat
They inhabit humid tropical rainforests, mossy ground, rocky outcrops, and areas near small streams. They prefer shaded, moist environments with plenty of hiding spaces.
Diet
Blue Poison Dart Frogs feed on ants, termites, small beetles, mites, and tiny invertebrates, obtaining their chemical toxins from alkaloid-rich prey items.
27. Yellow-Banded Poison Dart Frog
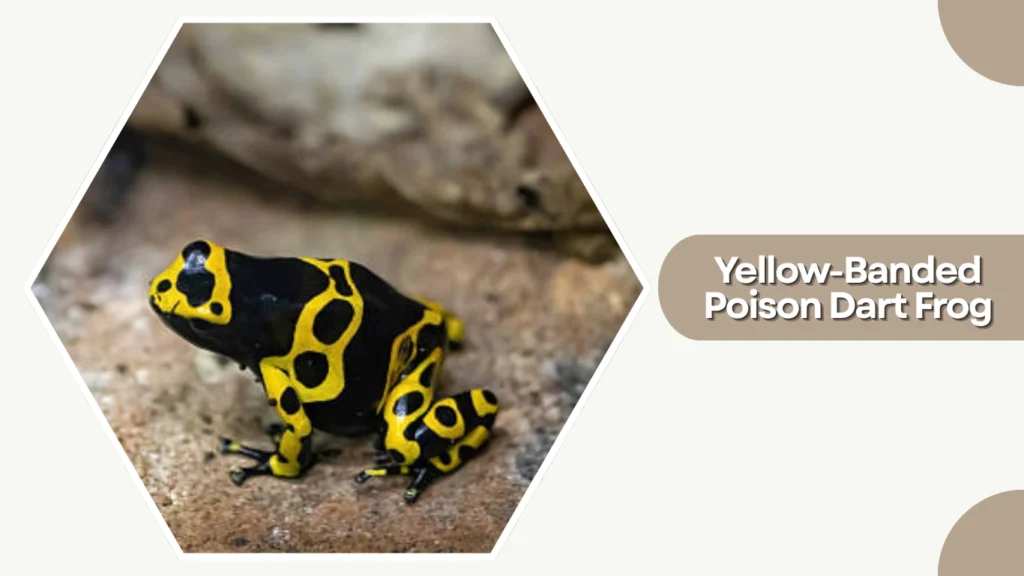

The Yellow-Banded Poison Dart Frog is a boldly patterned amphibian native to the rainforests of Venezuela. Its vivid black and yellow bands act as a warning signal to predators, emphasizing its toxic nature in the wild.
Identification
- Distinct alternating yellow and black bands
- Smooth, shiny skin
- Slender limbs with small toe pads
- Bright coloration that varies slightly among individuals
Size
Yellow-Banded Poison Dart Frogs typically measure 1 to 2 inches in length. Their compact bodies help them move quickly through leaf litter and dense vegetation.
Habitat
They inhabit humid lowland rainforests, mossy forest floors, and areas near streams, often remaining close to moist microhabitats. They hide under logs, leaves, and roots to maintain humidity.
Diet
Yellow-Banded Poison Dart Frogs feed on ants, mites, small beetles, termites, and tiny invertebrates, accumulating toxins from their specialized diet.
28. Waxy Monkey Tree Frog

The Waxy Monkey Tree Frog is a unique arboreal species native to South America, especially Brazil, Argentina, and Paraguay. It gets its name from its waxy skin secretions that help prevent dehydration in hot, sunny habitats.
Identification
- Light green to olive skin with a smooth, waxy texture
- Thick, muscular limbs resembling those of a monkey
- Large toe pads for gripping branches
- Distinct white line running along the sides of the body
Size
Waxy Monkey Tree Frogs typically measure 2.5 to 4 inches in length. Their robust limbs and sturdy bodies make them excellent climbers.
Habitat
They inhabit dry tropical forests, savannas, and scrublands, often perching in trees and shrubs. Their waxy coating allows them to tolerate more sunlight and drier conditions than most frogs.
Diet
Waxy Monkey Tree Frogs feed on insects, spiders, caterpillars, and other small invertebrates, hunting primarily at night while navigating branches and foliage.
29. Budgett’s Frog
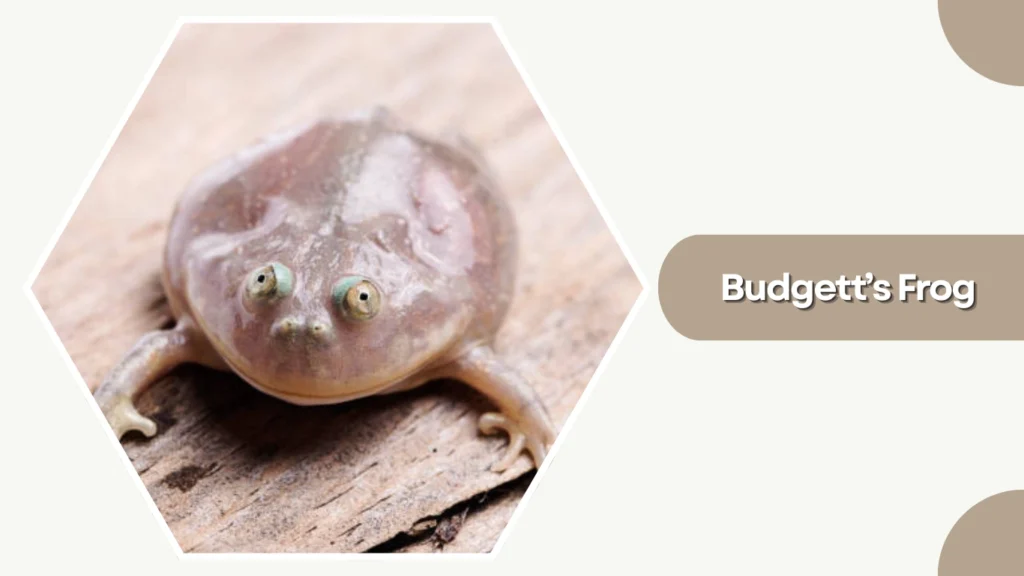

Budgett’s Frog, often called the “Hippo Frog,” is an unusual and comically shaped amphibian native to South America. Known for its wide mouth, flattened body, and loud screeching call, it is both fascinating and distinctive.
Identification
- Flattened, wide body with a large, gaping mouth
- Olive-green to brown coloration with mottled patterns
- Short limbs and a broad head
- Smooth skin with a slightly wrinkled appearance
Size
Budgett’s Frogs typically measure 4 to 6 inches in length. Their wide, bulky shape makes them appear even larger.
Habitat
They inhabit slow-moving waters, marshes, flooded grasslands, and temporary pools in Paraguay, Argentina, and Bolivia. They burrow into mud during dry seasons.
Diet
Budgett’s Frogs feed on fish, insects, worms, crustaceans, and even other frogs, capturing prey with powerful jaws and a rapid strike.
30. African Bullfrog

The African Bullfrog is one of the largest and most powerful frog species in the world, native to central and southern Africa. Known for its massive size and aggressive feeding behavior, it is a dominant predator in its habitat.
Identification
- Olive-green to muddy brown coloration
- Large, broad head with prominent jaw muscles
- Thick, robust body with strong limbs
- Males typically larger with a yellow or orange throat
Size
African Bullfrogs typically measure 4 to 9 inches in length, with some individuals weighing over 2 pounds. Males are significantly larger than females.
Habitat
They inhabit savannas, grasslands, marshes, and temporary rain-filled pools, often burrowing underground during dry seasons. They are highly adaptable and can survive drought by encasing themselves in a cocoon.
Diet
African Bullfrogs feed on insects, rodents, birds, reptiles, other frogs, and any prey they can overpower, using their strong jaws and quick strikes.
31. Darwin’s Frog
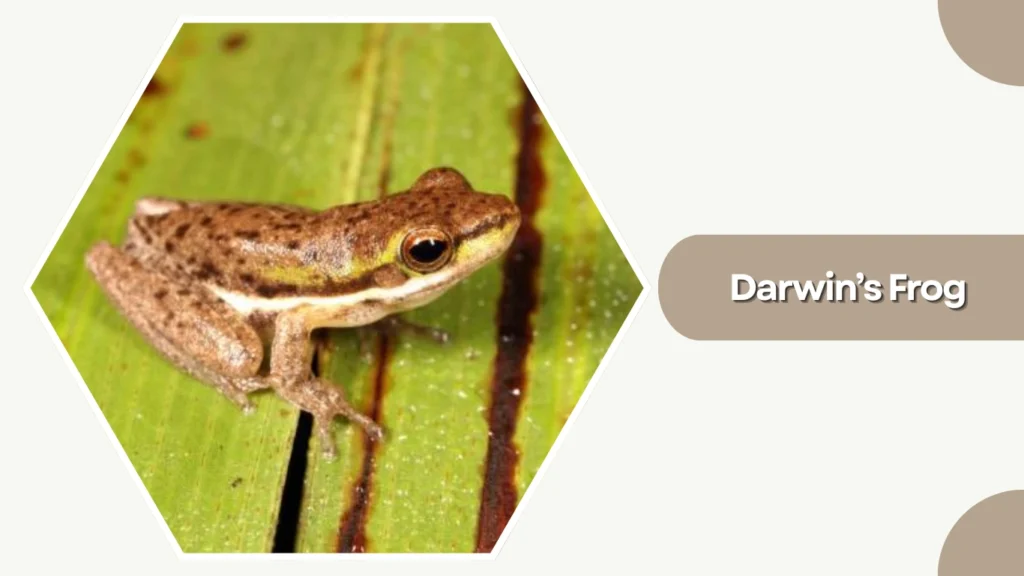

Darwin’s Frog is a small, leaf-mimicking amphibian native to Chile and Argentina. Famous for the male’s unique parenting method—carrying developing tadpoles in his vocal sac—it is one of the most unusual frog species in the world.
Identification
- Brown, green, or mottled body resembling a leaf
- Pointed, elongated snout
- Rough, textured skin
- Camouflaged coloration for forest floors
Size
Darwin’s Frogs typically measure 0.75 to 1.4 inches in length. Their small, lightweight bodies help them stay hidden among leaves and moss.
Habitat
They inhabit temperate forests, moist leaf litter, mossy ground, and areas near clear streams. Cool, shaded environments with high humidity are essential for their survival.
Diet
Darwin’s Frogs feed on ants, mites, small beetles, springtails, and tiny invertebrates, capturing prey with quick movements and a sticky tongue.
32. Malayan Horned Frog
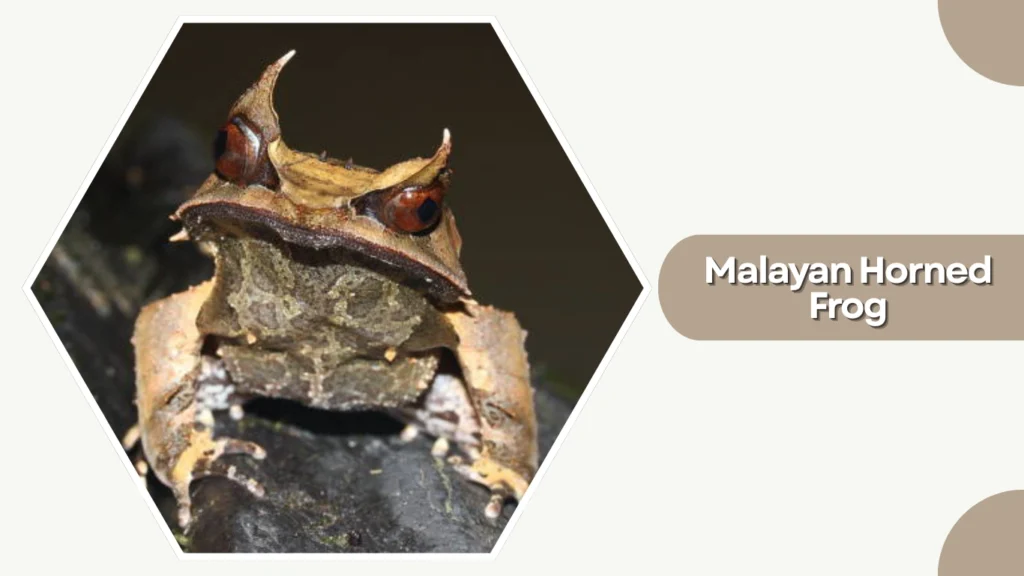

The Malayan Horned Frog is a master of camouflage, native to the rainforests of Southeast Asia. Its horn-like projections and leaf-like appearance allow it to blend perfectly into the forest floor.
Identification
- Triangular head with horn-like skin extensions above the eyes
- Leaf-shaped body with brown, tan, or reddish hues
- Rough, mottled skin mimicking leaf litter
- Large mouth and broad body
Size
Malayan Horned Frogs typically measure 4 to 5.5 inches in length. Their sizable, angular bodies enhance their camouflage among forest debris.
Habitat
They inhabit tropical rainforests, damp leaf litter, riverbanks, and dense forest floors, staying hidden among fallen leaves and branches to ambush prey.
Diet
Malayan Horned Frogs feed on insects, spiders, worms, small reptiles, and sometimes other frogs, relying on stealth and sudden strikes to capture prey.
33. Vietnamese Mossy Frog

The Vietnamese Mossy Frog is an exceptionally camouflaged species native to northern Vietnam. Its moss-like appearance allows it to blend seamlessly with wet, rocky surfaces and dense vegetation.
Identification
- Bumpy, uneven skin resembling green and black moss
- Irregular wart-like projections across the body
- Large toe pads for gripping rock surfaces
- Dark mottled coloration with patches of green
Size
Vietnamese Mossy Frogs typically measure 2.5 to 3.5 inches in length. Their compact, textured bodies enhance their camouflage in mossy habitats.
Habitat
They inhabit limestone caves, rocky pools, forested wetlands, and humid mountain streams, often clinging to wet rocks or hiding in crevices. High humidity and cool temperatures are essential.
Diet
Vietnamese Mossy Frogs feed on insects, spiders, worms, and small invertebrates, capturing prey with quick tongue strikes while remaining partially hidden.
34. Clown Tree Frog
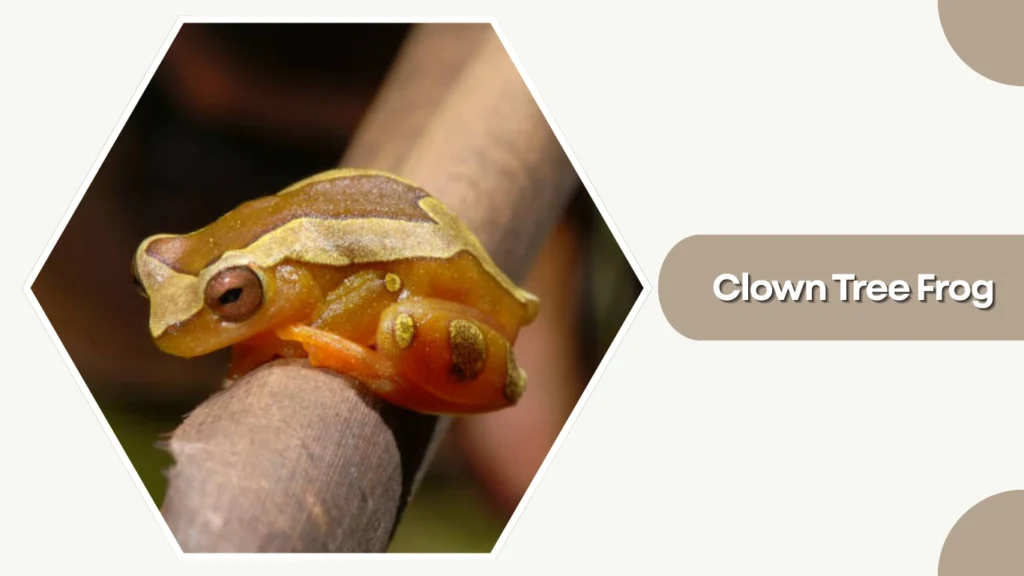

The Clown Tree Frog is a colorful, medium-sized amphibian native to the tropical regions of South America. Its bold patterns and bright markings give it a playful, clown-like appearance.
Identification
- Brown, tan, or reddish body with bright yellow or orange spots
- Distinct dark markings around the eyes
- Smooth skin with a glossy sheen
- Strong toe pads for climbing vegetation
Size
Clown Tree Frogs typically measure 1.5 to 2.5 inches in length. Their light, agile build makes them excellent climbers and jumpers.
Habitat
They inhabit tropical rainforests, forest edges, riverbanks, and areas with dense vegetation, often staying high in trees and shrubs. They prefer warm, humid environments with access to water for breeding.
Diet
Clown Tree Frogs feed on insects, flies, moths, beetles, small spiders, and other invertebrates, actively hunting at night among branches and foliage.
35. Red-Legged Frog

The Red-Legged Frog is a medium-sized amphibian native to western North America, known for the distinctive reddish coloring on its hind legs. It is a key species in wetland ecosystems and is currently threatened in some regions.
Identification
- Brown, reddish-brown, or olive body with dark spots
- Notable red or pinkish coloring on the hind legs
- Smooth skin with subtle mottling
- Prominent dorsolateral folds running down the back
Size
Red-Legged Frogs typically measure 2 to 5 inches in length. Their slim yet sturdy bodies allow for strong swimming and jumping.
Habitat
They inhabit ponds, marshes, slow-moving streams, wetlands, and damp forests, often preferring areas with dense vegetation and shaded water sources. They rely on permanent or semi-permanent water for breeding.
Diet
Red-Legged Frogs feed on insects, worms, spiders, snails, and small aquatic invertebrates, capturing prey both on land and in shallow water.
36. Mountain Yellow-Legged Frog

The Mountain Yellow-Legged Frog is a high-elevation amphibian native to the mountains of California. Recognized for its yellow-tinted legs and patterned skin, it is one of the most endangered frogs in North America.
Identification
- Yellow or yellow-orange coloring on the legs and underside
- Mottled brown, green, or gray body with irregular markings
- Smooth but slightly loose skin
- Slender limbs with partially webbed feet
Size
Mountain Yellow-Legged Frogs typically measure 1.5 to 3.3 inches in length. Their compact build suits the cold, alpine environments they inhabit.
Habitat
They inhabit high-altitude lakes, cold streams, alpine meadows, and rocky basins in the Sierra Nevada and Transverse Ranges. They rely on clean, cold, fishless water for breeding and survival.
Diet
Mountain Yellow-Legged Frogs feed on aquatic insects, larvae, small crustaceans, beetles, flies, and other invertebrates, foraging both in water and along rocky shorelines.
37. Green and Black Poison Dart Frog
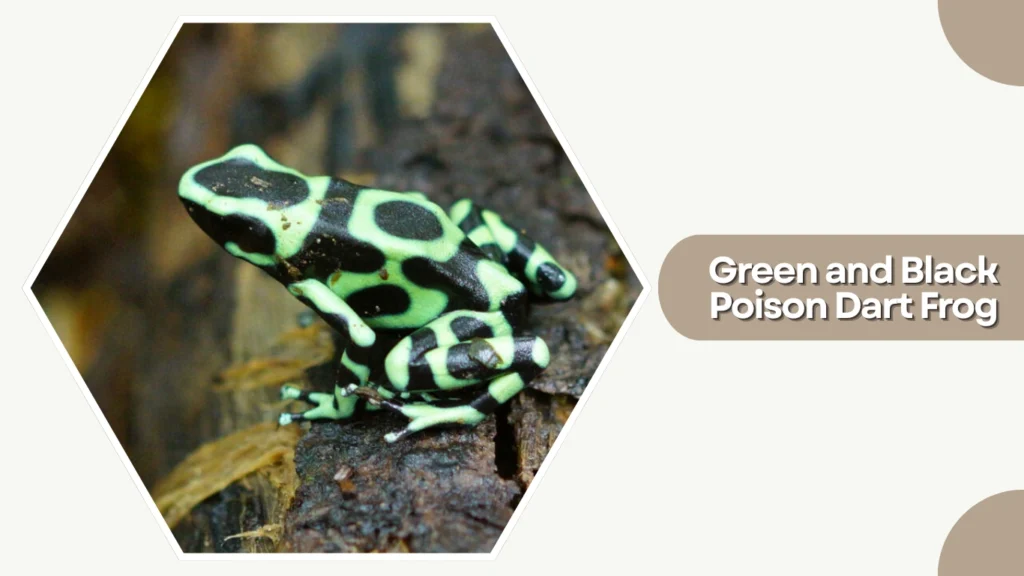

The Green and Black Poison Dart Frog is a boldly patterned amphibian native to Central and South America. Its striking colors serve as a warning to predators, indicating the presence of potent skin toxins.
Identification
- Bright green, turquoise, or mint-colored patches
- Contrasting black or dark brown irregular bands
- Smooth, glossy skin
- Small, agile body with quick movement
Size
Green and Black Poison Dart Frogs typically measure 1 to 1.5 inches in length. Their lightweight build allows them to navigate leaf litter and dense vegetation with speed.
Habitat
They inhabit humid tropical rainforests, shaded forest floors, mossy areas, and regions near small streams, preferring consistently moist microhabitats that prevent dehydration.
Diet
Green and Black Poison Dart Frogs feed on ants, tiny beetles, mites, termites, and other minute invertebrates, accumulating their toxins through their specialized prey.
38. Spotted Chorus Frog
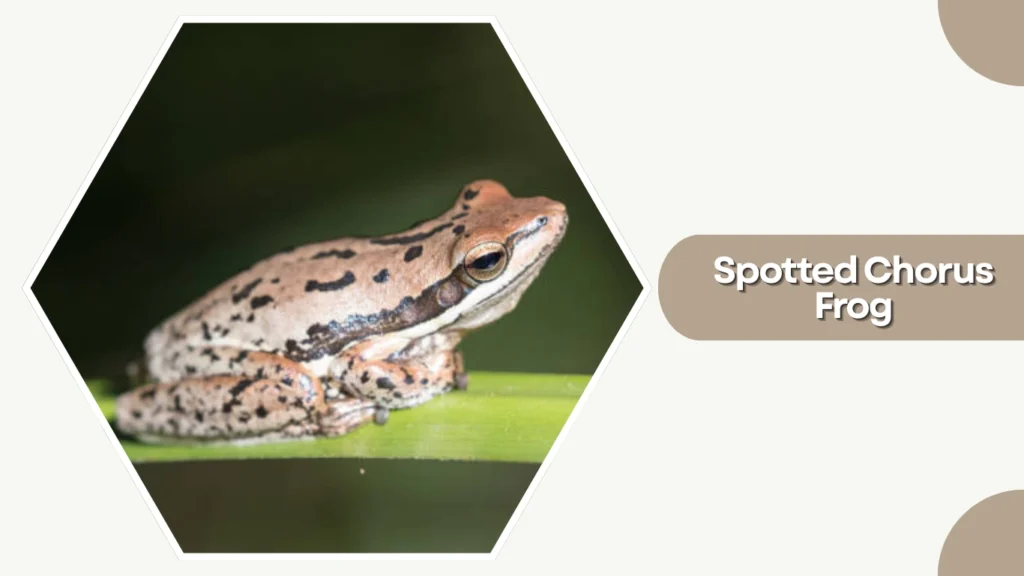

The Spotted Chorus Frog is a small, lively amphibian native to the central United States. Its distinctive spots and loud nighttime calls make it easy to identify during the breeding season.
Identification
- Light green, gray, or tan body with dark round spots
- Smooth to slightly granular skin
- Dark stripe running through the eye
- Small toe pads for limited climbing
Size
Spotted Chorus Frogs typically measure 0.75 to 1.5 inches in length. Their tiny bodies are well suited for hiding in grasses and shallow vegetation.
Habitat
They inhabit prairies, grasslands, temporary ponds, roadside ditches, and marshy fields, preferring areas with shallow water for breeding.
Diet
Spotted Chorus Frogs feed on small insects, flies, beetles, ants, spiders, and other tiny invertebrates, hunting mostly at night near moist vegetation.
39. Desert Rain Frog

The Desert Rain Frog is a small, round-bodied amphibian native to the coastal deserts of Namibia and South Africa. Known for its squeaky vocalizations and sand-burrowing lifestyle, it thrives in one of the driest frog habitats on Earth.
Identification
- Plump, rounded body with translucent, pale sandy skin
- Short limbs and a flat, wide head
- Bulging eyes positioned high on the head
- Smooth skin with minimal patterning, matching desert sands
Size
Desert Rain Frogs typically measure 1.5 to 2.5 inches in length. Their compact, pudgy build helps conserve moisture in arid environments.
Habitat
They inhabit coastal dunes, sandy deserts, scrublands, and areas with fog moisture, relying heavily on underground burrows to avoid heat and dehydration. They emerge primarily at night or during foggy conditions.
Diet
Desert Rain Frogs feed on termites, beetles, ants, larvae, and small invertebrates, capturing prey on the sand surface before retreating to their burrows.
40. White-Lipped Frog
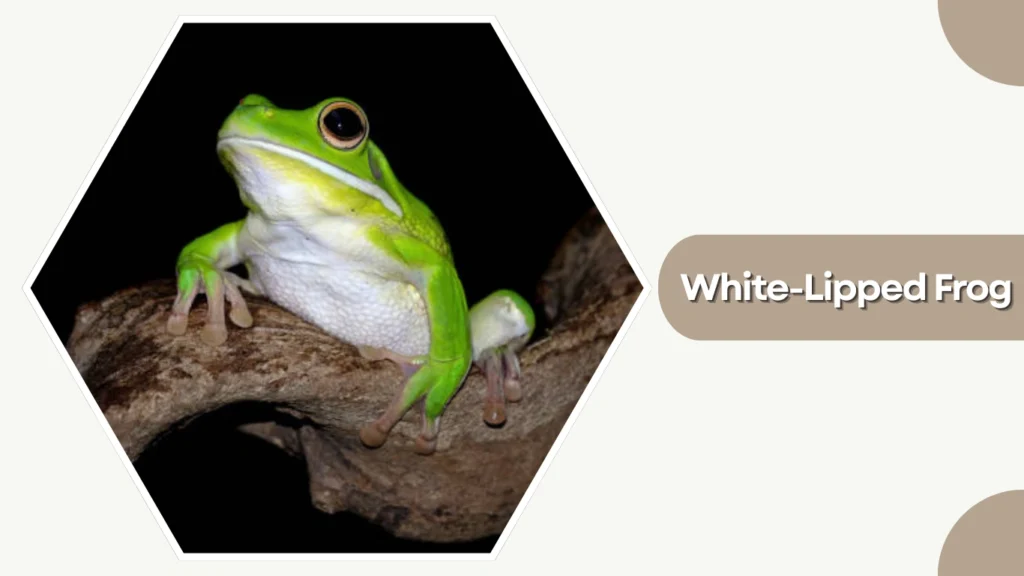

The White-Lipped Frog is a vibrant amphibian native to Southeast Asia and the Pacific islands. Its bright coloration and distinctive white stripe around the mouth make it easy to identify in dense tropical vegetation.
Identification
- Bright green body with smooth skin
- Distinct white or cream-colored stripe encircling the mouth
- Long limbs with strong toe pads for climbing
- Slim, agile build with minimal patterning
Size
White-Lipped Frogs typically measure 2.5 to 4 inches in length. Their slender bodies and long legs make them excellent climbers and jumpers.
Habitat
They inhabit tropical rainforests, wetlands, mangroves, gardens, and forest edges, often seen perched on leaves, branches, and vegetation near water sources. High humidity and warm temperatures are essential for their survival.
Diet
White-Lipped Frogs feed on insects, moths, beetles, flies, spiders, and small invertebrates, actively hunting at night among foliage and moist ground.
41. Smoky Jungle Frog

The Smoky Jungle Frog is a large, powerful amphibian native to Central and South America. Known for its deep calls and defensive behaviors, it is one of the largest frog species in its region.
Identification
- Brown, reddish-brown, or gray body with dark mottling
- Smooth to slightly granular skin
- Large, muscular limbs and broad head
- Prominent eyes and strong jaw structure
Size
Smoky Jungle Frogs typically measure 4 to 7 inches in length, with some individuals growing even larger. Their robust build supports fast movement on land and strong defensive postures.
Habitat
They inhabit tropical rainforests, riverbanks, swamps, and humid forest floors, often sheltering under logs, leaf litter, and burrows. They prefer warm, moist environments with access to shallow water.
Diet
Smoky Jungle Frogs feed on insects, small mammals, reptiles, amphibians, and invertebrates, using rapid strikes and strong jaws to overpower large prey.
42. Australian Green Tree Frog

The Australian Green Tree Frog is a calm, robust species native to Australia, New Guinea, and nearby islands. Its friendly demeanor and bright green coloration make it one of the most recognizable frogs worldwide.
Identification
- Smooth, bright green to blue-green skin
- Stocky, “dumpy” body shape
- Large toe pads adapted for climbing
- Occasional white or gold speckling along the back
Size
Australian Green Tree Frogs typically measure 3 to 4.5 inches in length. Their plump build and strong limbs allow them to navigate both trees and human dwellings with ease.
Habitat
They inhabit rainforests, woodlands, wetlands, and even homes and gardens, often sheltering in trees, pipes, roofs, and shaded structures. They prefer warm, humid environments but tolerate a range of conditions.
Diet
Australian Green Tree Frogs feed on insects, spiders, moths, roaches, and small invertebrates, occasionally consuming smaller frogs. Their sticky tongues and patient ambush behavior make them effective nighttime hunters.